As previously mentioned I have been reading over some of my old blog posts. A bit narcissistic I grant you, but I'm quite proud of some of the posts and after not rereading them for a few years they read rather better than I thought they would. One of those I landed on was a WW1 air combat post, which of course meant I read all of the others on that topic. Reading them two things came to mind, firstly I never did post the amendments I made to the original SPI rules and secondly where the hell did I put my notes and rules! Worry not, I did find them, eventually.
The starting point was the old SPI game "Flying Circus". I played this to death back in the mid 1970's when it first came out. So I suppose it was only natural that I would want to tinker with the concepts it through up. The original rules for that game can be found here
and if you want to follow what I did you should take a look at them. Like the majority of SPI games it used a hex gridded playing area but I didn't want to have to draw a large hex grid so I simply based the models on hexagonal bases and measured everything with a cardboard hex tool I made. You can see that in photo one. Aircraft don't stay in grid alignment with each other so when measuring line of sight and shooting ranges and arcs anything that crosses any part of the models base is 'on target'.
 |
The measuring tool used for movement....
|
 |
| ...and for gun range checks |
The original rules are three dimensional in so far as aircraft can climb and dive in the vertical plane but not much more, all other movement is in 2 dimensions within a height band of 1,000 feet, as you would expect from a map and counters game I suppose. I wanted to add some out of plane manoeuvres like rolls and Immelmann turns that were the key tactics in aerial combat. Other things needed adding as well like energy gain and loss too. The original game had one thing going for it though, which was that it could be learned in a couple of minutes! Each aeroplane had a stall speed and top speed defined as movement points. Making a turn used up movement points and different planes took different numbers of turns to climb to the next height level. You could only shoot at a target which was within range and that had been in your firing arc for half of your, or their movement points. Possible damage varied depending on the number of machine guns (single or twin) and the ammunition feed (belt or drum). Lastly you had a limited number of turns firing and drum fed guns had to change the drum after two turns of firing. That was pretty much it, a real beer and pretzels game.
Luckily smarter minds than mine had already looked at some of the things I felt needed improving so I borrowed and adapted. First I changed the combat resolution table outcomes so they reflected pilot morale and experience by having most hits impact not the aircraft but the pilots confidence with any hit having a chance of causing a critical damage result which would have an effect on the aeroplane. As I said in the original posts those early aeroplanes were mostly a lot of nothing wrapped in canvas and wood, the vital systems were a small percentage of the target area. Talking about the aeroplanes the original game only had statistics for around 20 of them, mostly allied types. That needed expanding which given the lack of firm data on early combat aeroplanes was a big (read huge) task. The amendments I ended up with are as follows.
Flying Circus Plus
These
adaptions use a mix of advanced flying Circus (SPI), Richtofen’s War (AH) and
home brew rules.
Turn Sequence (IGOYGO)
1.
Player 1 spotting
2.
Player 1 Movement
3.
Player 2 spotting
4.
Both player’s firing
Repeat the above for Player 2
Simultaneous Movement
codes
Each turn note the aeroplanes movement on the
play sheet using the following codes:
·
Number – that number of
hexes straight ahead
·
Down Arrow – dive note
how many metres
·
Up arrow climb - note how
many metres (Max of 100 per hex)
·
R or L one hex side turn
in indicated direction in the current hex one letter per hex side subject to a
max of three.
·
Special manoeuvres – use
code as shown below.
Diving
There are two standard categories of dive and a special manoeuvre available in
FCP. The two standard dives are:
Shallow dive
– there is no reduction in MP for a shallow dive each 2MP spent moving a
shallow dive loses 100 feet. Turns may
be made while shallow diving.
Steep- dive
– an aircraft may only move straight ahead in a steep dive. Each hex costs 2MP and loses 150 feet a steep
dive. Aircraft gain KE while steep
diving.
Power Dive –
see special manoeuvres.
Over Speeding (gaining
energy)
Additional “speed” may be gained as a result of gaining energy by diving under
power (over speed). There is a maximum
safe over speed before structural damage is risked. This varies between aircraft as shown on the
statistics sheet. The original game rule
of diving at a reduced speed is not used in the advanced rules. Aircraft may dive at the maximum normal level
flight speed or faster (due to energy gain) without any restrictions, but may
suffer structural damage.
Gaining kinetic energy
(KE)
Where an
aircraft dives at its maximum speed or above it will gain kinetic energy (over
speed) up to its maximum over speed allowance.
Aircraft gain one MP per KE point gained per turn spent diving at or
over maximum speed.
Using KE
Once an aircraft has ended its dive it still holds the excess energy which must
be bled off. This happens in one of two
ways. In each turn of level flight KE
movement points are lost in addition to any other speed reduction (through
Drag). Alternatively, the excess energy
may be used to “zoom and boom”. This
entails converting excess energy (over speed movement points) into additional
climb points. One KE point provides an
additional 200 feet of climb.
Damage from diving at
over speed
Aircraft diving
at more than safe dive speed risk structural damage. Different aircraft have different safe dive
speeds. This is shown on the statistics
chart. The structural damage modifier
will increase depending on how much they have exceeded the safe maximum dive
speed. Use the over speed damage table
to check if damage occurs.
Damage
from high stress manoeuvres
Where an aircraft
performs a high stress manoeuvre roll on hit chart CRT3 to see if damage
occurs. First dice to see if hits are
scored. If so pilot resolution is not
reduced as with MG fire instead move on to a critical damage test as per gun
fire. Ignore all results other than
structural damage. If there is
structural damage check on the structural damage table for the type of damage
incurred. Fragile aircraft use range 1,
normal range 2 and robust range 3 result columns.
Fragile
Aircraft
Certain aircraft are
considered fragile and have an increased chance of suffering structural
failures when undertaking high stress manoeuvres. Fragility is noted on the data chart for
those aircraft. They have lower
resistance to structural critical damage than normal.
Loss of
height and turns
Any turn in a single hex after the first hex side creates a loss of height of
50 feet
Front MG
Arc of fire (simultaneous movement)
As firing solutions
are harder to achieve with simultaneous movement the frontal arc of fire is
widened. It is now as shown below.
This
simulates the ability to ‘kick in’ a little rudder to yaw the aeroplane. Range remains the same.
Arc of Fire
Gunner operated ring and pin mounted guns
The gunner has to
anticipate the pilot’s actions which can interfere with tracking
targets. He may also need to switch
targets rapidly from left to right above or below. To simulate this gunners fire at -1 on
the CRT dice roll for all targets other than those below their aircraft where
they fire at -2.
Spotting
Any aircraft firing
is automatically spotted by the target aircraft. Aircraft in blind spots cannot be
spotted. Line of sight is required to
spot. Clouds block line of sight. Otherwise roll 2D6 at the start of the turn and
adjust the result as follows (all factors are cumulative)
|
Aircraft firing weapons
|
+1
|
|
Aircraft within 8 hexes
|
+1
|
|
Aircraft below spotter
|
-1
|
|
Aircraft ‘up sun’
|
-2
|
|
Aircraft over 20 hexes from spotter
|
-2
|
If the
result is 7 or more the aircraft is spotted.
Any other aircraft in close formation are also spotted. Close formation means in base to base contact
and at the same height (+/- 200 feet).
If playing IGOYGO non-moving player’s aircraft check after the moving
player has completed all movement
Ranges in
3D firing and spotting
To simulate firing in
three dimensions the enemy aircraft must be within 1,000 feet above or below
and not in a blind spot. Only aeroplanes
with the prop hang special move may fire directly upwards, and those with power
dive fire directly below and only when those special manoeuvres have been used
to gain the firing solution. The chart
below gives the actual range in hexes to use on the CRT
|
Height
Diff’ (feet)
|
Hexes to target >
|
|
0
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
|
0
|
-
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
|
200
|
1
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
|
400
|
2
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
|
600
|
3
|
3
|
4
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
-
|
|
800
|
4
|
4
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
-
|
|
1,000
|
5
|
5
|
5
|
6
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
-
|
-
|
NB 200 feet height
difference equals one hex height difference in spotting
Combat damage and pilot
resolution
In FC an
aircraft has a damage limit equal to its speed.
Each point of damage reduces the aeroplanes speed by one point until it
falls below stall speed when it is considered destroyed. In these additional rules, particularly
strong aircraft have a damage level higher than their speed as shown in the
game statistics and fragile aircraft a lower value.
Firing uses
the tables below to ascertain if hits are scored. These do no damage to the aircraft but reduce
the pilot’s resolution (willingness to continue in combat). Lots of bullets passing through your ‘plane
will tend to do that. The amount scored
is subtracted from the resolution of the target pilot. Once his resolution reaches zero his
objective becomes survival and he will attempt to get off the board via any
friendly table side. Standard pilots
have a resolution of 10. Veterans and
novices may have their resolution adjusted as players see fit. In a campaign setting reduce resolution of
all pilots by 1 for each friend shot down and killed. Add 1 for each enemy aeroplane shot down to
the shooter who got the kill shot. Add 1
to all pilots who survive a game. It is
suggested that minimum resolution be set at 6 and maximum be capped at 18.
For damage
checks roll a second D6, if the result is equal or lower than the result on the
combat CRT add the totals rolled on both dice together and check the critical
damage table.
For example:
a Fokker DVII (Twin belt fed MGs) fires at an SE5a at a range of 3 hexes. A D6 is thrown scoring a 5 resulting in 2
hits. The SE5a pilot’s resolution is
reduced by 2. As hits were scored a
second D6 is thrown this results in a roll of 2 this is equal to the CRT score
of 2 hits. Critical damage may have
occurred. Adding the two dice rolls
together gives a total of 7. This is a
control hit, checking on the control hit table requires a final roll of a
single D6 this scores a 1 which reduces the SE5a’s turn code to the next lowest
level.
Long
Bursts
A player may opt to fire a ‘Long Burst’ before rolling the dice. This adds 1 to the to hit di roll. It uses up double ammunition and cannot be
used if there is insufficient ammunition remaining or for drum fed guns there
is only one ammunition point left before needing to reload. After using a long burst roll 1D6 on a 1 the
guns used have jammed and if this is the main gun, the pilot takes a reduction
of 1 to his resolution for not being able to shoot. This remains in place for the rest of the
game. Each following combat turn where
the aircraft has flown straight and level for the entire turn roll 1D6 and
unjam on a 6.
Special
manoeuvres
These are all
moves which require a climb or dive but which do not follow the FC rules so
they are treated as special exceptions to the movement rules. Some of these special manoeuvres are
considered high stress manoeuvres and may lead to structural damage. This will be detailed on each aeroplane’s
data card. To understand the moves the
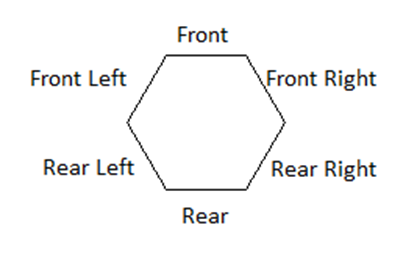
direction and facing of the aeroplane will use the descriptions in the image
below. Front is always the initial direction of movement.
1. Side Slip (Code -SS) -The aeroplane remains pointing in
the same direction throughout the manoeuvre. It moves into the Front Right or Front Left
adjacent hex at a cost of 2MP and loses 50 feet of height. The action may be repeated as long as there
are MP available to use. Alternating
from right to left or left to right is permitted.
2. Yo-Yos (Code HYY or LYY + number of
hexes) -A Yo-yo
allows an aeroplane to reduce distance over ground by alternatively climbing
and diving. A Yo-yo may start with a
climb or a dive but must alternate climbs and dives in each successive hex
during the manoeuvre. The first step is
always by entering the adjacent front hex.
It uses the energy gained in a dive to recover some of the height lost in
the following climb. Each hex moved
through costs 2MP. A hex in which the
aeroplane dives reduces height by 100 feet.
A hex in which the aeroplane climbs gains 50 feet. The manoeuvre may be carried out while flying
in a straight line or combined with turns.
3. Hammerhead turn (Code HT) – HIGH STRESS. The aeroplane moves forward one hex and
enters a vertical climb. it then
revolves around the aircraft’s length (going from nose vertically up to
vertically down) it then dives vertically in the same hex. The aircraft may exit to any adjacent
hex. The manoeuvre costs 6MP. For targeting purposes 3 MP may count towards
acquiring a target for the aeroplane carrying out the action and all 6 for an
aeroplane attempting to shoot at it. While carrying out this manoeuvre the
aeroplane hangs almost stationary at the top of the climb and any aircraft
firing at it does so with a +1 modifier to the to hit dice roll.
4. Rolling reversal (Code RR) –HIGH STRESS a half loop and
roll out the modern Immelmann turn.
5. Full loop (Code O) – The maximum size of the loop and
so the number of hexes displaced to the rear is determined by the aeroplane’s
rate of climb. The aeroplane ends the
manoeuvre facing in the same direction and the noted number of hexes to the
rear of the starting hex. The ‘plane
will lose 50 metres of height in the loop.
|
Rate of climb
|
MP cost
|
End point
|
|
50
|
2
|
Start hex
|
|
100
|
4
|
1 hex to rear
|
|
150
|
6
|
2 hexes to rear
|
|
200
|
8
|
3 hexes to the rear
|
|
250
|
10
|
4 Hexes to the rear
|
|
300
|
12
|
5 hexes to the rear
|
6. Displacement roll (Code DR) – In essence this is a combination
of a side slip and a roll to slow forward movement while maintaining MP. The aircraft moves forwards two hexes at a
cost of 4MP
7. Propeller hang (Code PH) HIGH STRESS– Aircraft moves forwards one hex and
enters a vertical climb it then stays in the same hex but is assumed to be
pointing vertically. As with a
Hammerhead The manoeuvre costs 6MP. For
targeting purposes 3 MP may count towards acquiring a target for the aeroplane
carrying out the action and all 6 for an aeroplane attempting to shoot at it.
While carrying out this manoeuvre the aeroplane hangs almost stationary at the
top of the climb and any aircraft firing at it does so with a +1 modifier to
the to hit dice roll. After the
propeller hang the aircraft may carry out a further propeller hang, a
hammerhead or a rolling reversal
8. Power Dive (Code PD) – HIGH STRESS The aircraft
moves forwards one hex and then enters a vertical dive. It gains KE in the dive at double the normal
rate. To end the power dive the aircraft
enters a normal dive for half a turn and then level flight for half a turn. Fragile aircraft check for structural damage
on pulling out.
Charts
CRT 1 (twin MG belt fed)
|
Die/Range
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
2
|
2
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
3
|
4
|
2
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
4
|
4
|
3
|
2
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
|
5
|
5
|
4
|
2
|
2
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
|
6
|
6
|
5
|
3
|
2
|
2
|
2
|
2
|
1
|
CRT 2 (Double MG – drum fed)
|
Die/Range
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
2
|
2
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
3
|
3
|
2
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
4
|
4
|
2
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
5
|
4
|
3
|
2
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
|
6
|
5
|
4
|
3
|
2
|
2
|
2
|
1
|
1
|
CRT 3 (Single MG belt fed)
|
Die/Range
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
2
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
3
|
2
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
4
|
2
|
2
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
5
|
3
|
2
|
2
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
|
6
|
3
|
3
|
2
|
2
|
2
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
CRT 4 (Single MG drum fed)
|
Die/Range
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
2
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
3
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
4
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
5
|
2
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
|
6
|
3
|
2
|
2
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
NOTE: Aircraft with both a single belt and single drum
fed forward machine gun (e.g. SE5A) use CRT1 until the drum is empty they then
use CRT3 until the drum is reloaded.
Critical Hit Chart
Throw a second D6 if the score is lower than the result on
the CDT above a critical hit has been scored.
Throw a second D6and add the scores together to get a score of 2 – 12
and check the table below.
|
Score
|
Effect
|
|
2
|
Crew Hit
|
|
3
|
Engine Hit
|
|
4
|
Structural
Damage
|
|
5
|
Structural
Damage
|
|
6
|
Control Hit
|
|
7
|
Control Hit
|
|
8
|
Control Hit
|
|
9
|
Structural
Damage
|
|
10
|
Structural
Damage
|
|
11
|
Engine Hit
|
|
12
|
Crew hit
|
Crew Hit
For multi crew aircraft dice to see which crew member is hit. Roll 1D6 1 or 2 is KIA all other results are
wounded.
Pilot hit if KIA aircraft is out of control and enters steep
dive until it hits the ground. If
wounded reduce resolution by 2. If
Gunner hit KIA that gun position is out of action for the rest of the
mission. If wounded reduce pilot
resolution by 2. All fire by that gunner
is at minus one to hit. Further wounds
to a previously wounded person reduce resolution by an additional 2 for each
wound.
Engine Hit
Throw 1D6
|
Score
|
Result
|
|
1
|
Engine
seizes. Power reduced to zero.
|
|
2
|
Oil leak
engine runs rough and seizes in next 6 turns 1D6 1 to seize then 1 & 2
etc.
|
|
3
|
Max power
reduced by 1
|
|
4
|
Max power
reduced by 2
|
|
5
|
Fire - 1
point of damage/resolution per turn until extinguished
|
|
6
|
Fire 2 points
of damage/resolution per turn until extinguished
|
Extinguishing fire – dive the aircraft in a steep dive. On a 6 on a D6 the fire is extinguished. In a power dive it is extinguished on a 5 or
6
Structural Damage
No effect until the next high stress manoeuvre is attempted. Then roll 1D6:
|
Score
|
Result
|
|
1
|
No Damage
|
|
2
|
No Damage
|
|
3
|
1D6 Damage
|
|
4
|
2D6 Damage
|
|
5
|
May no longer
make high stress manoeuvres as a wing spar has cracked
|
|
6
|
Aircraft
disintegrates
|
High Stress Manoeuvres are:
·
Steep Dive
·
Any turn of more than one hex side or part hex
side after the first.
·
A second turn in a consecutive hex after the
first hex in the same turn
·
Special Manoeuvres as noted
Control Damage
Throw 1D6
|
Score
|
Result
|
|
1
|
Turn Rate reduces to next lower rate (e.g.
A to B or C to D)
|
|
2
|
Unable to turn to Left
|
|
3
|
Unable to turn to Right
|
|
4
|
Climb cost increased by 1D6 steps
|
|
5
|
May only shallow dive
|
|
6
|
May only gentle climb
|
No Special Manoeuvres may be used that require a move no
longer available as a result of Control damage
Over speed effects
Throw 1D6 add any adjustment for how much over speed the aircraft is
|
Score
|
Result
|
|
1
|
No effect
|
|
2
|
No effect
|
|
3
|
1 Point
Damage
|
|
4
|
2 Points
Damage
|
|
5
|
3 Points
Damage – possible structural damage test on next high stress manoeuvre
|
|
6
|
4 Points
Damage - wing spars crack no steep dives or climbs
|
|
7 to 11
|
Severe damage
wings detach plane breaks up
|
You don't have everything you need here (yet). Next post I will put up the playing sheet on which the aircraft data is recorded and explain the abbreviations on that. I will also post the data for the aeroplanes most commonly seen over the western front. That will be another long post!